When installing flowmeters, users may have questions like how to connect pipe and flowmeter, the relationship of outer/ inner diameter of pipe and connector, how to choose the correct size of connectors, and etc.
1. LORRIC’s PPH and PVDF connectors conform to ISO standards.
LORRIC manufactures PPH and PVDF hot welding connectors according to ISO standards.
(1). The material of PPH,SDR11 butt fusion fitting and socket fusion fitting.
ISO 15494 specifies the characteristics and requirements for components such as pipes, fittings, and valves made from one of the following materials intended to be used for thermoplastics piping systems in the field of industrial applications above and below ground: polybutene (PB), polyethylene (PE), polyethylene of raised temperature resistance (PE-RT), crosslinked polyethylene (PE-X) and polypropylene (PP). (Citing source: https://www.nen.nl/en/nen-en-iso-15494-2018-en-252186)
*There are many materials defined in the standard. The content related to ISO 15494 provided here is only applicable to the material and regulations of polypropylene (PP) .
(2). The material of PVDF,SDR21 S10 butt fusion fitting and socket fusion fitting.
ISO 10931 specifies the plastics piping systems for industrial applications- specifications for components and the system of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). (Citing source: https://www.iso.org/standard/36773.html)
▲Go back to the Outline of this Article
2. An Index of pressure resistance and strength. The standard dimension ratio (SDR) and pipe series (S).
The standard dimension ratio(SDR) and pipe series(S) describe the correlation between the pipe dimension and the thickness of the pipe wall. Pipes with a lower SDR or S can withstand higher pressures. It is a method of rating a pipe's durability against pressure.
Attention: Due to the different mechanical strength of each material, SDR can only be compared in the same material, and different materials of SDR cannot be compared.
▲Go back to the Outline of this Article
3. PPH, PVDF pipe size
(1). PPH pipe size (mm)
|
Nominal outside diameter dn
|
Wall thickness, e, and associated tolerance, a |
| Pipe series S and standard dimension ratio SDR |
S 20
SDR 41 |
S 16
SDR 33 |
S 12.5
SDR 26 |
S 8.3
SDR 17.6 |
S 8
SDR 17 |
S 5
SDR 11 |
S 3.2
SDR 7.4 |
S 2.5
SDR 6 |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
e
min |
b |
| 12 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.0 |
+0.4 |
| 16 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.2 |
+0.5 |
2.7 |
+0.5 |
| 20 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
2.8 |
+0.5 |
3.4 |
+0.6 |
| 25 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.3 |
+0.5 |
3.5 |
+0.6 |
4.2 |
+0.7 |
| 32 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
2.9 |
+0.5 |
4.4 |
+0.7 |
5.4 |
+0.8 |
| 40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.3 |
+0.5 |
2.4 |
+0.5 |
3.7 |
+0.6 |
5.5 |
+0.8 |
6.7 |
+0.9 |
| 50 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.0 |
+0.4 |
2.9 |
+0.5 |
3.0 |
+0.5 |
4.6 |
+0.7 |
6.9 |
+0.9 |
8.3 |
+1.1 |
| 63 |
1.8 |
+0.4 |
2.0 |
+0.4 |
2.5 |
+0.5 |
3.6 |
+0.6 |
3.8 |
+0.6 |
5.8 |
+0.8 |
8.6 |
+1.1 |
10.5 |
+1.3 |
| 75 |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
2.3 |
+0.5 |
2.9 |
+0.5 |
4.3 |
+0.7 |
4.5 |
+0.7 |
6.8 |
+0.9 |
10.3 |
+1.3 |
12.5 |
+1.5 |
| 90 |
2.2 |
+0.5 |
2.8 |
+0.5 |
3.5 |
+0.6 |
5.1 |
+0.8 |
5.4 |
+0.8 |
8.2 |
+1.1 |
12.3 |
+1.5 |
15.0 |
+1.7 |
| 110 |
2.7 |
+0.5 |
3.4 |
+0.6 |
4.2 |
+0.7 |
6.3 |
+0.9 |
6.6 |
+0.9 |
10.0 |
+1.2 |
15.1 |
+1.8 |
18.3 |
+2.1 |
| 125 |
3.1 |
+0.6 |
3.9 |
+0.6 |
4.8 |
+0.7 |
7.1 |
+1.0 |
7.4 |
+1.0 |
11.4 |
+1.4 |
17.1 |
+2.0 |
20.8 |
+2.3 |
| 140 |
3.5 |
+0.6 |
4.3 |
+0.7 |
5.4 |
+0.8 |
8.0 |
+1.0 |
8.3 |
+1.1 |
12.7 |
+1.5 |
19.2 |
+2.2 |
23.3 |
+2.6 |
| 160 |
4.0 |
+0.6 |
4.9 |
+0.7 |
6.2 |
+0.9 |
9.1 |
+1.2 |
9.5 |
+1.2 |
14.6 |
+1.7 |
21.9 |
+2.4 |
26.6 |
+2.9 |
| 180 |
4.4 |
+0.7 |
5.5 |
+0.8 |
6.9 |
+0.9 |
10.2 |
+1.3 |
10.7 |
+1.3 |
16.4 |
+1.9 |
24.6 |
+2.7 |
29.9 |
+3.2 |
| 200 |
4.9 |
+0.7 |
6.2 |
+0.9 |
7.7 |
+1.0 |
11.4 |
+1.4 |
11.9 |
+1.4 |
18.2 |
+2.1 |
27.4 |
+3.0 |
33.2 |
+3.6 |
| 225 |
5.5 |
+0.8 |
6.9 |
+0.9 |
8.6 |
+1.1 |
12.8 |
+1.5 |
13.4 |
+1.6 |
20.5 |
+2.3 |
30.8 |
+3.3 |
37.4 |
+4.0 |
| 250 |
6.2 |
+0.9 |
7.7 |
+1.0 |
9.6 |
+1.2 |
14.2 |
+1.7 |
14.8 |
+1.7 |
22.7 |
+2.5 |
34.2 |
+3.7 |
- |
- |
| 280 |
6.9 |
+0.9 |
8.6 |
+1.1 |
10.7 |
+1.3 |
15.9 |
+1.8 |
16.6 |
+1.9 |
25.4 |
+2.8 |
38.3 |
+4.1 |
- |
- |
| 315 |
7.7 |
+1.0 |
9.7 |
+1.2 |
12.1 |
+1.5 |
17.9 |
+2.0 |
18.7 |
+2.1 |
28.6 |
+3.1 |
43.1 |
+4.6 |
- |
- |
| 355 |
8.7 |
+1.1 |
10.9 |
+1.3 |
13.6 |
+1.6 |
20.1 |
+2.3 |
21.1 |
+2.4 |
32.2 |
+3.5 |
48.5 |
+5.1 |
- |
- |
| 400 |
9.8 |
+1.2 |
12.3 |
+1.5 |
15.3 |
+1.8 |
22.7 |
+2.5 |
23.7 |
+2.6 |
36.3 |
+3.9 |
54.7 |
+5.7 |
- |
- |
| 450 |
11.0 |
+1.3 |
13.8 |
+1.6 |
17.2 |
+2.0 |
25.5 |
+2.8 |
26.7 |
+2.9 |
40.9 |
+4.3 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 500 |
12.3 |
+1.5 |
15.3 |
+1.8 |
19.2 |
+2.2 |
28.3 |
+3.1 |
29.7 |
+3.2 |
45.4 |
+4.8 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 560 |
13.7 |
+1.6 |
17.2 |
+2.0 |
21.4 |
+2.4 |
31.7 |
+3.4 |
33.2 |
+3.6 |
50.8 |
+5.3 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 630 |
15.4 |
+1.8 |
19.3 |
+2.2 |
24.1 |
+2.7 |
35.7 |
+3.8 |
37.4 |
+4.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 710 |
17.4 |
+2.0 |
21.8 |
+2.4 |
27.2 |
+3.0 |
40.2 |
+4.3 |
42.1 |
+4.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 800 |
19.6 |
+2.2 |
24.5 |
+2.7 |
30.6 |
+3.3 |
45.3 |
+4.8 |
47.4 |
+5.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 900 |
22.0 |
+2.4 |
27.6 |
+3.0 |
34.4 |
+3.7 |
51.0 |
+5.3 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1000 |
24.5 |
+2.7 |
30.6 |
+3.3 |
38.2 |
+4.1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1200 |
29.4 |
+3.2 |
36.7 |
+3.9 |
45.9 |
+4.8 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1400 |
34.3 |
+3.7 |
42.9 |
+4.5 |
53.5 |
+5.6 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 1600 |
39.2 |
+4.2 |
49.0 |
+5.1 |
61.2 |
+6.4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
a: All dimensions correspond to those given in ISO 4065.
b: The tolerances have been calculated from the expression (0.1e + 0.2) mm and rounded up to the nearest 0.1 mm. |
(2). PVDF pipe size (mm)
|
Nominal outside diameter
dn
|
Wall thickness, e, and associated tolerance, b |
| Pipe series S and standard dimension ratio SDR |
S 16
SDR 33 |
S 10
SDR 21 |
S 8
SDR 17 |
S 6.3
SDR 13.6 |
| e |
a |
e |
a |
e |
a |
e |
a |
| 8 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 10 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 12 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 16 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 20 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 25 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.9 |
+0.4 |
| 32 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2.4 |
+0.5 |
| 40 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2.4 |
+0.5 |
- |
- |
| 50 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
3.0 |
+0.6 |
- |
- |
| 63 |
2.0 |
+0.5 |
3.0 |
+1.5 |
3.8 |
+0.6 |
- |
- |
| 75 |
2.3 |
+0.5 |
3.6 |
+1.5 |
4.5 |
+0.7 |
- |
- |
| 90 |
2.8 |
+0.5 |
4.3 |
+1.5 |
5.4 |
+0.8 |
- |
- |
| 110 |
3.4 |
+0.6 |
5.3 |
+1.5 |
6.6 |
+0.9 |
- |
- |
| 125 |
3.9 |
+0.6 |
6.0 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 140 |
4.3 |
+0.7 |
6.7 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 160 |
4.9 |
+0.7 |
7.7 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 180 |
5.5 |
+0.8 |
8.6 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 200 |
6.2 |
+0.9 |
9.6 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 225 |
6.9 |
+0.9 |
10.8 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 250 |
7.7 |
+1.0 |
11.9 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 280 |
8.6 |
+1.1 |
13.4 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 315 |
9.7 |
+1.2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 355 |
10.9 |
+1.3 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 400 |
12.3 |
+1.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
*For safety reasons, the minimum wall thickness should be not less than 1,9 mm.
Tolerances of the wall thickness: (0,1 e + 0,2) mm, rounded up to the nearest 0,1 mm.
All dimensions correspond to those of ISO 4065. |
▲Go back to the Outline of this Article
4. Common pipe connection for PPH and PVDF connectors
1. Butt welding
Steps of butt welding: Heat up both sides of the two different pipes which are going to be connected until both are a bit melted. Then completely connect both melted surfaces. Wait until they cool down, then the butt welding is done. Due to it's not using part of the pipe to do the insertion, butt welding is a way to save more material. Moreover, to compare with other ways, it will cause minimal leakage and is more pressure resistant. For butt welding, users need to be aware that the thickness and diameter of both pipes should be similar which will make the connection more solid.
(1). Dimensions of spigot ends for PVDF butt fusion fittings
e: The wall thickness, e, of the spigot end (over the length, Lb1) corresponds to the PVDF pipe size (see Table 3.(1).)
Lb1: min. inside tubular length of fusion end, comprising initial depth of spigot end necessary for butt fusion.
Lb2: min. outside tubular length of fusion end, comprising initial length of fusion end.
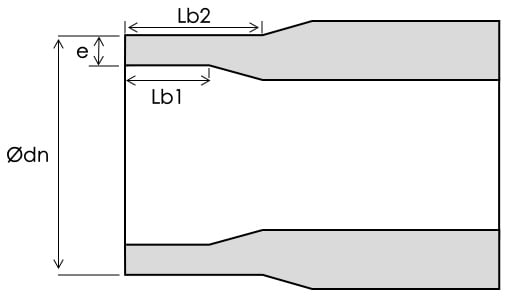
Nominal outside diameter
dn |
Inside tubular length*
Lb1 |
Outside tubular length*
Lb2 |
| 8 |
4 |
10 |
| 10 |
4 |
10 |
| 12 |
4 |
10 |
| 16 |
4 |
10 |
| 20 |
4 |
10 |
| 25 |
4 |
10 |
| 32 |
5 |
10 |
| 40 |
5 |
10 |
| 50 |
5 |
12 |
| 63 |
6 |
12 |
| 75 |
6 |
12 |
| 90 |
7 |
12 |
| 110 |
8 |
12 |
| 125 |
8 |
15 |
| 140 |
9 |
15 |
| 160 |
9 |
20 |
| 180 |
10 |
20 |
| 200 |
11 |
20 |
| 225 |
12 |
25 |
| 250 |
13 |
25 |
| 280 |
14 |
30 |
| 315 |
15 |
30 |
| *For bends, a reduction of the tubular length(s) is permissible. |
(2). Dimensions of spigot ends for PPH butt fusion fittings
e: The wall thickness, e, of the spigot end (over the length, Lb1) corresponds to the PPH pipe size (see Table 3.(1).)
Lb1: inside length of spigot end.
Lb2: outside length of spigot end.
Nominal outside diameter
dn |
Inside tubular length*
Lb1 |
Outside tubular length*
Lb2 |
| 12 |
4 |
10 |
| 16 |
4 |
10 |
| 20 |
4 |
10 |
| 25 |
4 |
10 |
| 32 |
5 |
10 |
| 40 |
5 |
10 |
| 50 |
5 |
12 |
| 63 |
6 |
12 |
| 75 |
6 |
12 |
| 90 |
7 |
12 |
| 110 |
8 |
12 |
| 125 |
8 |
15 |
| 140 |
9 |
15 |
| 160 |
9 |
20 |
| 180 |
10 |
20 |
| 200 |
11 |
20 |
| 225 |
12 |
25 |
| 250 |
13 |
25 |
| 280 |
14 |
30 |
| 315 |
15 |
30 |
| 355 |
16 |
30 |
| 400 |
18 |
30 |
| 450 |
20 |
35 |
| 500 |
20 |
35 |
| 560 |
20 |
40 |
| 630 |
20 |
40 |
| 710 |
20 |
40 |
| 800 |
20 |
50 |
| 900 |
20 |
50 |
| 1000 |
20 |
60 |
| 1200 |
20 |
60 |
| 1400 |
20 |
70 |
| 1600 |
20 |
70 |
| *For bends, a reduction in the length(s) of the tubular part(s) of the is permissible. |
2. Socket Weld
Connecting process: Melt the outer surface of one tube while simultaneously melting the inner surface of the other tube and then insert the melted surface of both tubes while they are still hot, keeping them in the same position until they are cooled down and completely fixed together. It is critical to note that the outer diameter of one tube must be equal to the inner diameter of the other tube so they can be firmly joined together after melting and cooling down. Pay attention as well to the inner and outer diameters and the thickness of the wall of the tubes because one tube will be inserted to the inside of the other tube.In addition, the extension length of the inserted pipe, for example for a Ø20 pipe, the extension length should be greater than 10mm and the heat should be directly applied to the tube in order to maintain the same size and be melted within a specific time.
dn: nominal outside diameter
ds1: inside diameter of socket mouth
ds2: inside diameter of socket root, i.e. the inside diameter of a circular plane parallel to the plane of the socket mouth and located a distance Ls (the reference socket length) from the socket mouth
ds3 min: minimum diameter of flow channel (bore) through body of fitting
Ls: reference socket length, i.e. the theoretical minimum socket length used for calculation purposes
Ls1: actual length of socket, i.e. the distance from the socket mouth to the shoulder
Ls2: heated length of socket, i.e. the depth of penetration of the heated tool into the socket
Ls3: insertion length, i.e. the depth of penetration of the pipe into the socket
Ls4: heated length of pipe, i.e. the depth of penetration of the pipe into the heated tool
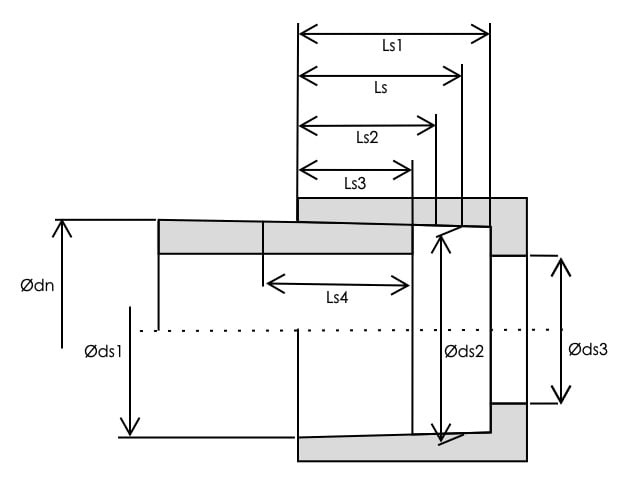
2. 1. Diameters and lengths of sockets for socket fusion fittings of PVDF (ISO 10931)
|
Nominal outside diameter
dn
|
Mean outside diameter of pipe
dem |
Mean inside diameter |
|
min
|
max
|
Socket mouth
ds1 |
Socket root
ds2 |
| min |
f |
min |
f |
| 16.0 |
15.8 |
16.0 |
15.2 |
+0.3 |
15.1 |
+0.3 |
| 20.0 |
19.8 |
20.2 |
19.2 |
+0.3 |
19.0 |
+0.3 |
| 25.0 |
24.8 |
25.0 |
24.2 |
+0.3 |
23.9 |
+0.4 |
| 32.0 |
31.8 |
32.0 |
31.1 |
+0.4 |
30.9 |
+0.4 |
| 40.0 |
39.8 |
40.0 |
39.0 |
+0.4 |
38.8 |
+0.4 |
| 50.0 |
49.8 |
50.0 |
48.9 |
+0.5 |
48.7 |
+0.5 |
| 63.0 |
62.7 |
63.0 |
61.9 |
+0.6 |
61.6 |
+0.5 |
| 75.0 |
74.7 |
75.0 |
73.7 |
+0.5 |
73.4 |
+0.5 |
| 90.0 |
89.7 |
90.0 |
88.6 |
+0.6 |
88.2 |
+0.6 |
| 110.0 |
109.6 |
110.0 |
108.4 |
+0.6 |
108.0 |
+0.6 |
2. 2. Diameters and lengths of sockets for socket fusion fittings of PPH (ISO 15494)
| Diameters and lengths of sockets of type A socket fusion fittings where no machining of the outside surface of the pipe. |
|
Nominal outside diameter
dn
|
Mean outside diameter of pipe
dem |
Mean inside diameter |
|
min
|
Socket mouth
ds1m |
Socket root
ds2m |
| min |
f |
min |
f |
| 16.0 |
16.0 |
15.2 |
+0.3 |
15.1 |
+0.3 |
| 20.0 |
20.0 |
19.2 |
+0.3 |
19.0 |
+0.3 |
| 25.0 |
25.0 |
24.2 |
+0.3 |
23.9 |
+0.4 |
| 32.0 |
32.0 |
31.1 |
+0.4 |
30.9 |
+0.4 |
| 40.0 |
40.0 |
39.0 |
+0.4 |
38.8 |
+0.4 |
| 50.0 |
50.0 |
48.9 |
+0.5 |
48.7 |
+0.5 |
| 63.0 |
63.0 |
61.9 |
+0.6 |
61.6 |
+0.5 |
| 75.0 |
75.0 |
74.3 |
+0.6 |
73.1 |
+0.6 |
| 90.0 |
90.0 |
89.3 |
+0.6 |
87.9 |
+0.6 |
| 110.0 |
110.0 |
108.4 |
+0.6 |
107.7 |
+0.6 |
▲Go back to the Outline of this Article
Contact Us
Products you may also like